In this tutorial, we will also have a look at the express framework. This framework is built in such a way that it acts as a minimal and flexible Node.js web application framework, providing a robust set of features for building single and multipage, and hybrid web application.
What is Express.js?
Express.js is a Node js web application server framework, which is specifically designed for building single-page, multi-page, and hybrid web applications.
It has become the standard server framework for node.js. Express is the backend part of something known as the MEAN stack.
The MEAN is a free and open-source JavaScript software stack for building dynamic web sites and web applications which has the following components;
1) MongoDB - The standard NoSQL database
2) Express.js - The default web applications framework
3) Angular.js - The JavaScript MVC framework used for web applications
4) Node.js - Framework used for scalable server-side and networking applications.
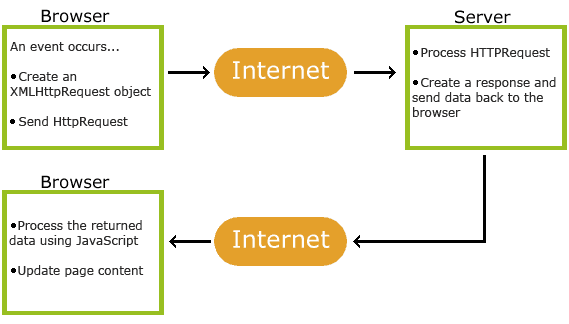
The Express.js framework makes it very easy to develop an application which can be used to handle multiple types of requests like the GET, PUT, and POST and DELETE requests. Installing and using ExpressExpress gets installed via the Node Package manager. This can be done by executing the following line in the command line
Express.js is a Node js web application server framework, which is specifically designed for building single-page, multi-page, and hybrid web applications.
It has become the standard server framework for node.js. Express is the backend part of something known as the MEAN stack.
The MEAN is a free and open-source JavaScript software stack for building dynamic web sites and web applications which has the following components;
1) MongoDB - The standard NoSQL database
2) Express.js - The default web applications framework
3) Angular.js - The JavaScript MVC framework used for web applications
4) Node.js - Framework used for scalable server-side and networking applications.
The Express.js framework makes it very easy to develop an application which can be used to handle multiple types of requests like the GET, PUT, and POST and DELETE requests. Installing and using ExpressExpress gets installed via the Node Package manager. This can be done by executing the following line in the command line
npm install express
The above command requests the Node package manager to download the required express modules and install them accordingly.
- npm install express --save
create a simple server module which will listen on port no 3000. In this example, if a request is made through the browser on this port no, then server application will send a 'Hello' World' response to the client.
Code Explanation:
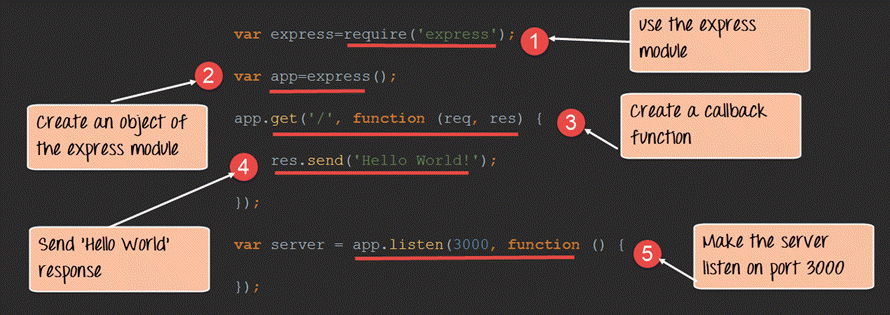
In our first line of code, we are using the require function to include the "express module."
Before we can start using the express module, we need to make an object of the express module.
Here we are creating a callback function. This function will be called whenever anybody browses to the root of our web application which is http://localhost:3000. The callback function will be used to send the string 'Hello World' to the web page.
modules which installed with express
var express=require('express');
var app=express();
app.get('/',function(req,res)
{
res.send('Hello World!');
});
var server=app.listen(3000,function() {});
Code Explanation:
In our first line of code, we are using the require function to include the "express module."
Before we can start using the express module, we need to make an object of the express module.
Here we are creating a callback function. This function will be called whenever anybody browses to the root of our web application which is http://localhost:3000. The callback function will be used to send the string 'Hello World' to the web page.
In the callback function, we are sending the string "Hello World" back to the client. The 'res' parameter is used to send content back to the web page. This 'res' parameter is something that is provided by the 'request' module to enable one to send content back to the web page.
We are then using the listen to function to make our server application listen to client requests on port no 8000. You can specify any available port over here.
Output:
We are then using the listen to function to make our server application listen to client requests on port no 8000. You can specify any available port over here.
Output:
modules which installed with express
- npm install body-parser -save
- npm install cookie-parser -save
- npm install multer --save