ER Diagram
The ER or (Entity Relational Model) is a high-level conceptual data model diagram. Entity-Relation model is based on the notion of real-world entities and the relationship between them.
ER modeling helps you to analyze data requirements systematically to produce a well-designed database. So, it is considered a best practice to complete ER modeling before implementing your database.
History of ER models
ER diagrams are a visual tool which is helpful to represent the ER model. It was proposed by Peter Chen in 1971 to create a uniform convention which can be used for relational database and network. He aimed to use an ER model as a conceptual modeling approach.
Entity relationship diagram displays the relationships of entity set stored in a database. In other words, we can say that ER diagrams help you to explain the logical structure of databases. At first look, an ER diagram looks very similar to the flowchart. However, ER Diagram includes many specialized symbols, and its meanings make this model unique.
- ER model allows you to draw Database Design
- It is an easy to use graphical tool for modeling data
- Widely used in Database Design
- It is a GUI representation of the logical structure of a Database
- It helps you to identifies the entities which exist in a system and the relationships between those entities
Why use ER Diagrams?
Here, are prime reasons for using the ER Diagram
- Helps you to define terms related to entity relationship modeling
- Provide a preview of how all your tables should connect, what fields are going to be on each table
- Helps to describe entities, attributes, relationships
- ER diagrams are translatable into relational tables which allows you to build databases quickly
- ER diagrams can be used by database designers as a blueprint for implementing data in specific software applications
- The database designer gains a better understanding of the information to be contained in the database with the help of ERP diagram
- ERD is allowed you to communicate with the logical structure of the database to users
Components of the ER Diagram
This model is based on three basic concepts:
- Entities
- Attributes
- Relationships

A real-world thing either living or non-living that is easily recognizable and nonrecognizable. It is anything in the enterprise that is to be represented in our database. It may be a physical thing or simply a fact about the enterprise or an event that happens in the real world
An entity can be place, person, object, event or a concept, which stores data in the database. The characteristics of entities are must have an attribute, and a unique key. Every entity is made up of some 'attributes' which represent that entity.
Relationship
Relationship is nothing but an association among two or more entities.Entities take part in relationships. We can often identify relationships with verbs or verb phrases.
Attributes
It is a single-valued property of either an entity-type or a relationship-type.
For example, a lecture might have attributes: time, date, duration, place, etc.
An attribute is represented by an Ellipse

Simple attribute ;-- Simple attributes can't be divided any further. For example, a student's contact number. It is also called an atomic value
Composite attribute:-- It is possible to break down composite attribute. For example, a student's full name may be further divided into first name, second name, and last name.
Derived attribute:-- This type of attribute does not include in the physical database. However, their values are derived from other attributes present in the database. For example, age should not be stored directly. Instead, it should be derived from the DOB of that employee.
Multivalued attribute:-- Multivalued attributes can have more than one values. For example, a student can have more than one mobile number, email address, etc
Weak Entities
A weak entity is a type of entity which doesn't have its key attribute. It can be identified uniquely by considering the primary key of another entity. For that, weak entity sets need to have participation.
A weak entity is a type of entity which doesn't have its key attribute. It can be identified uniquely by considering the primary key of another entity. For that, weak entity sets need to have participation.
Cardinality
Defines the numerical attributes of the relationship between two entities or entity sets.
Different types of cardinal relationships are:
- One-to-One Relationships
- One-to-Many Relationships
- May to One Relationships
- Many-to-Many Relationships
One entity from entity set X can be associated with at most one entity of entity set Y and vice versa.
Example: One student can register for numerous courses. However, all those courses have a single line back to that one student.
2.One-to-many:
One entity from entity set X can be associated with multiple entities of entity set Y, but an entity from entity set Y can be associated with at least one entity.
3. Many to One
More than one entity from entity set X can be associated with at most one entity of entity set Y. However, an entity from entity set Y may or may not be associated with more than one entity from entity set X.
4. Many to Many:
One entity from X can be associated with more than one entity from Y and vice versa
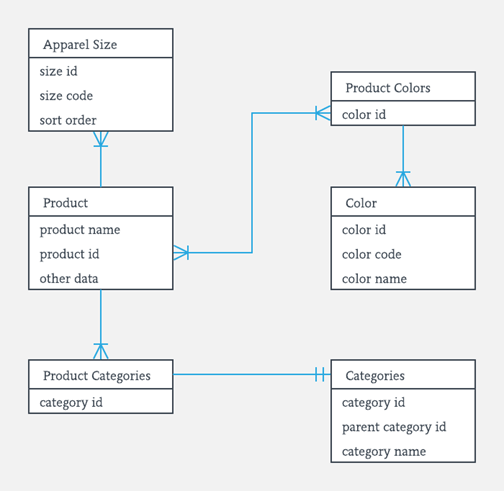
ER- Diagram Notations
ER- Diagram is a visual representation of data that describe how data is related to each other.



No comments:
Post a Comment